OpenCV의 이미지와 영상 처리
OpenCV 특징
- 인텔이 초기 개발 주도
- Windows, linux, Mac OS X, 안드로이드, i-OS 등 다양한 플랫폼에서 사용 가능
- 방대한 컴퓨터 비전 관련 라이브러리와 손쉬운 인터페이스 제공
OpenCV 이미지 로딩
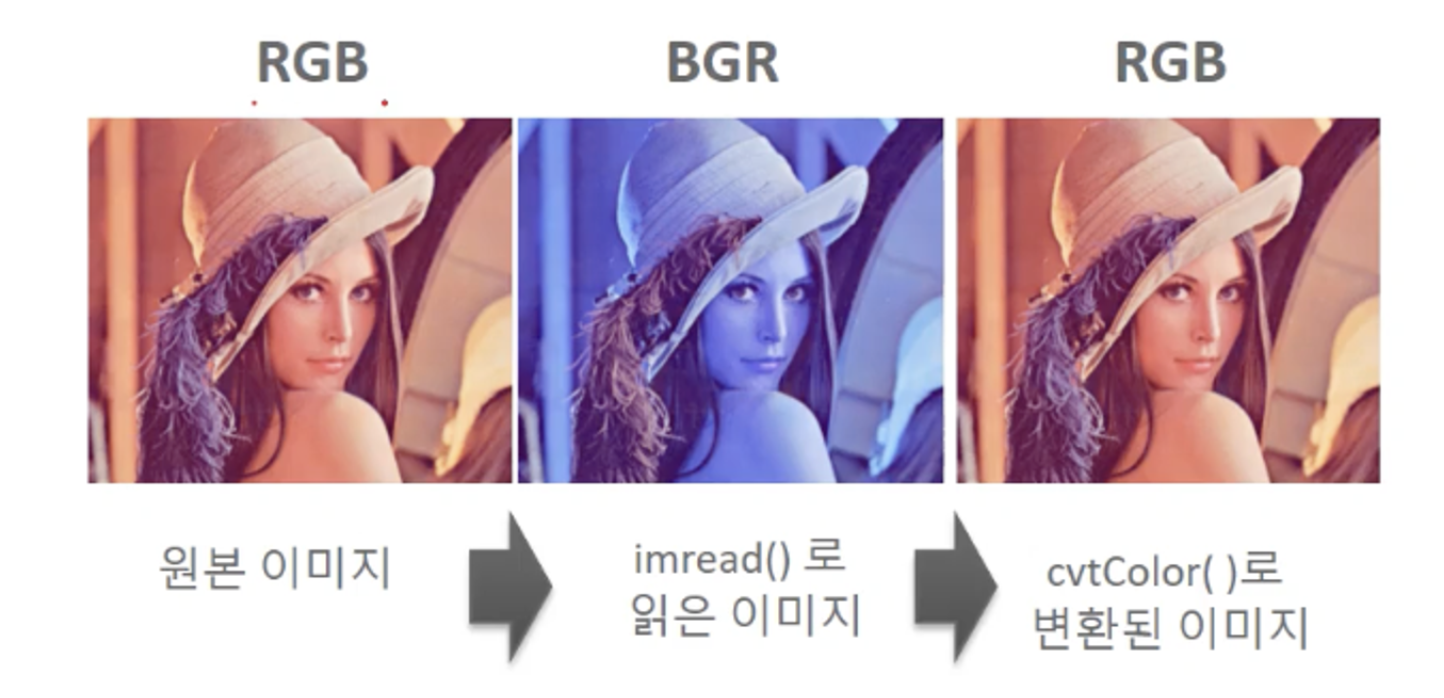
imread()를 이용한 이미지 로딩
- OpenCV에서 이미지 로딩은
imread(’파일명’)을 이용. imread(’파일명’)은 파일을 읽어 넘파이 array로 변환 - OpenCV에서 imread()를 이용하여 이미지 로딩 시 가장 주의해야 할 점은 OpenCV가 이미지를 RGB 형태가 아닌 BGR 형태로 로딩하기 때문에 색감이 원본 이미지와 다르게 나타난다는 것임.
1
2
3
4
5
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img_array = cv2.imread('파일명')
plt.imshow(img_array)
OpenCV 이미지 로딩 시 BGR을 RGB로 변환
cvtColor()를 이용하여 BGR을 RGB로 변환
OpenCV에서 imread(’파일명’)을 이용하여 로딩된 이미지 배열은 BGR 형태의 배열이므로 이를 RGB 형태의 배열로 변환하려면 cvtColor(이미지 배열, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)를 이용함.
1
2
3
4
5
6
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
bgr_img_array = cv2.imread('파일명')
rgb_img_array = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_img_array,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img_array)
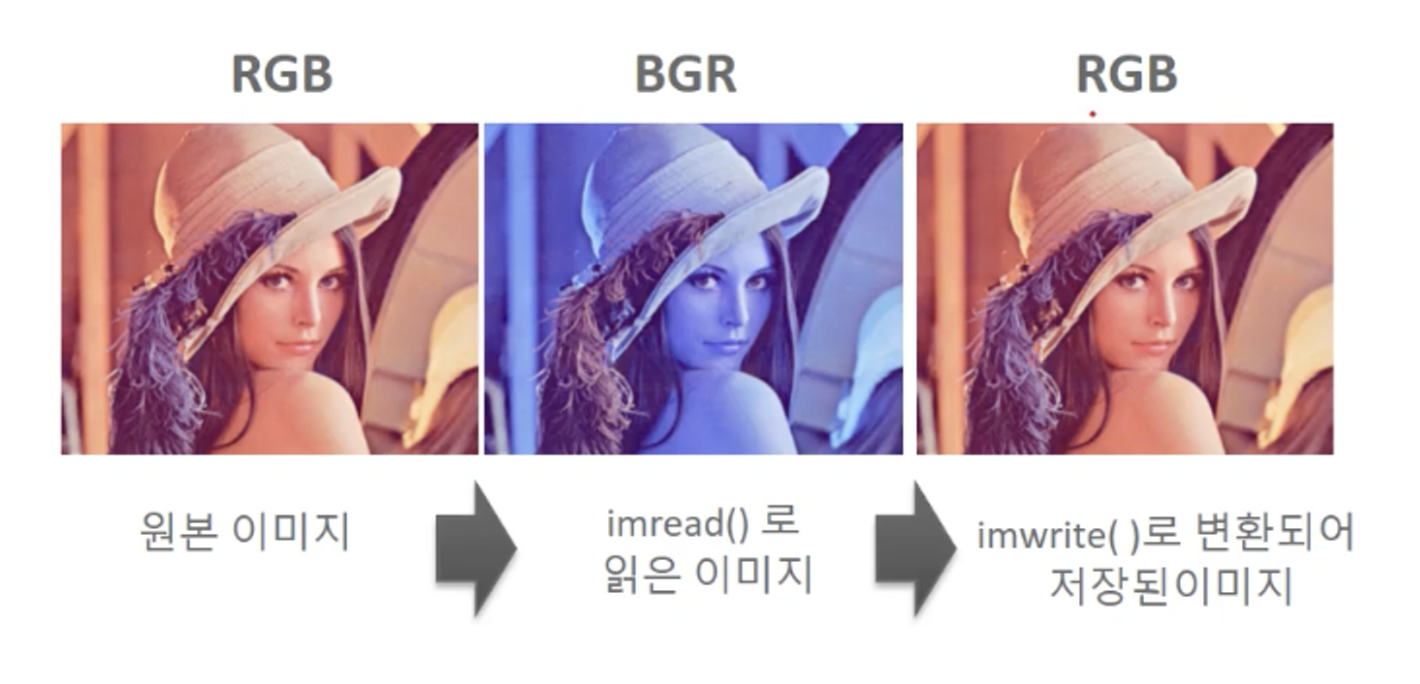
OpenCV 이미지 배열을 파일에 쓰기
imwrite()를 이용하여 파일에 쓰기
OpenCV에서 메모리에 있는 이미지 배열을 다시 파일에 저장하려면 imwrite(’출력파일명’, 이미지배열)을 이용함. 이때 imread()로 인해 BGR형태로 되어 있는 이미지 배열을 다시 RGB 형태로 변환하여 저장함. 따라서 imread()로 읽고, imwrite()로 출력한 이미지 파일은 다시 RGB 형태의 파일이 됨.
1
2
3
4
5
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img_array = cv2.imread('파일명')
cv2.imwrite('출력파일명',img_array)
OpenCV의 이미지와 영상 처리
skimage(사이킷이미지)로 이미지 로드 하기
• skimage는 imread()를 이용하여 RGB 원본 이미지를 RGB 형태의 넘파이 배열로 반환함.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from skimage import io
#skimage는 imread()를 이용하여 image를 numpy 배열로 반환함.
sk_image = io.imread('/content/data/beatles01.jpg')
print('sk_image type:', type(sk_image), ' sk_image shape:', sk_image.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(sk_image)
#plt.show()
OpenCV로 이미지 로드하기
- OpenCV는 imread()를 이용하여 원본 RGB 이미지를 BGR 형태의 넘파이 배열로 반환함.
- OpenCV의 imwrite()를 이용한다면 BGR 형태의 이미지 배열을 파일에 기록할 때 다시 RGB형태로 변환하므로 사용자는 RGB->BGR->RGB 변환에 신경쓰지 않아도 됨.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import cv2
cv2_image = cv2.imread('/content/data/beatles01.jpg')
cv2.imwrite('/content/data/beatles02_cv.jpg', cv2_image)
print('cv_image type:', type(cv2_image), ' cv_image shape:', cv2_image.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
img = plt.imread('/content/data/beatles02_cv.jpg')
plt.imshow(img)
#plt.show()
OpenCV의 imread()로 반환된 BGR 이미지 넘파이 배열을 그대로 시각화 하기
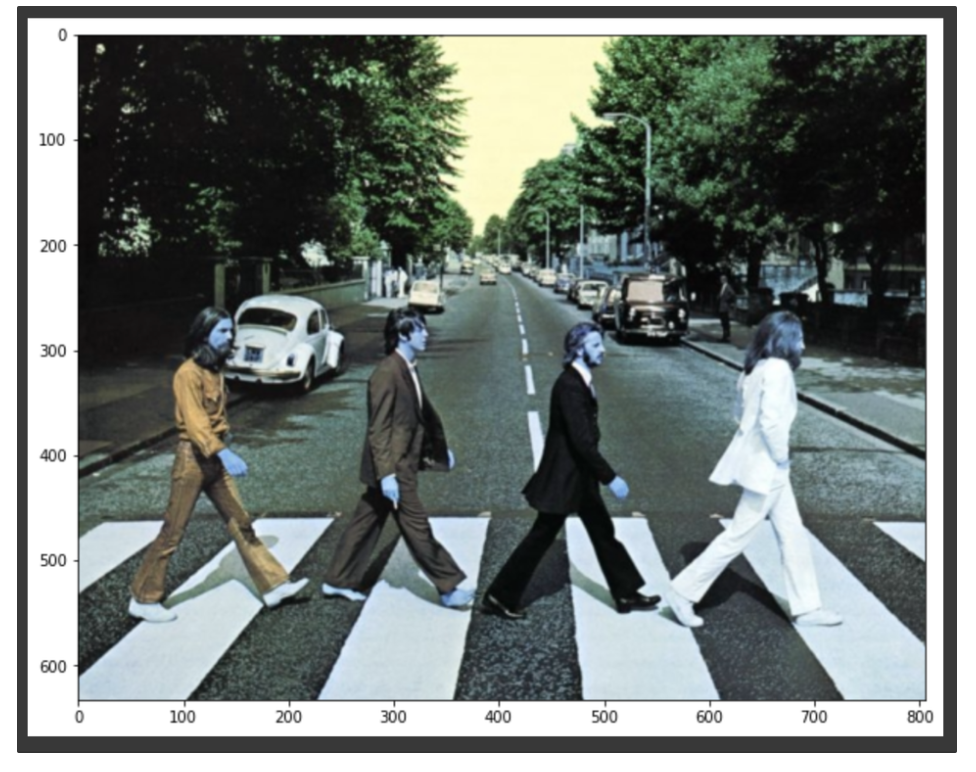
• OpenCV의 imread()는 RGB를 BGR로 변환하므로 원하지 않는 이미지가 출력됨
1
2
3
4
5
cv2_image = cv2.imread('/content/data/beatles01.jpg')
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(cv2_image)
plt.show()
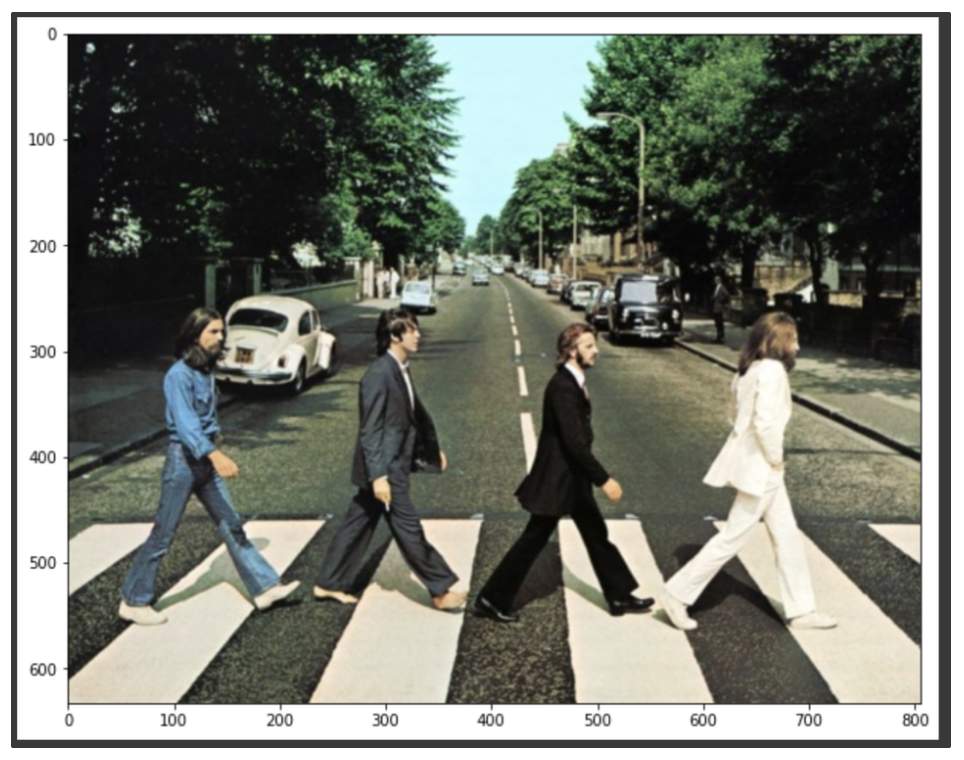
cvtColor(cv2_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)를 이용하여 RGB로 변경
1
2
3
4
5
6
cv2_image = cv2.imread('/content/data/beatles01.jpg')
draw_image = cv2.cvtColor(cv2_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(draw_image)
plt.show()
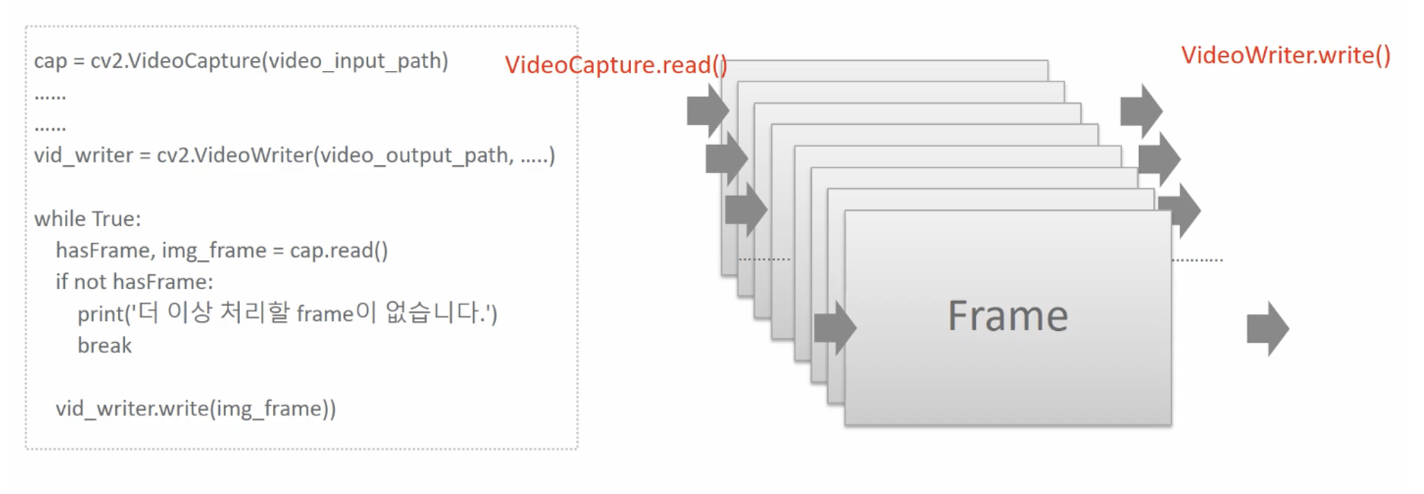
OpenCV 영상 처리 개요
OpenCV의 VideoCapture 클래스는 동영상을 개별 Frame으로 하나씩 읽어들이는 기능을 제공 VideoWriter는 VideoCapture로 읽어들인 개별 Frame을 동영상 파일로 Write 수행.
ex)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_input_path)
...
...
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(video.output_path,...)
while True:
hasFrame, img_frame = cap.read()
if not hasFrame:
print('더 이상 처리할 frame이 없습니다.')
break
vid_writer.write(img_frame)
VideoCapture 개요
VideoCaputer객체는 생성 인자로 입력 video 파일 위치를 받아 생성
- cap = cv2.VideoCaputer(video_input_path)
VideoCaputer객체는 입력 video 파일의 다양한 속성을 가져 올 수 있음
- 영상 Frame 너비 : cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)
- 영상 Frame 높이 : cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)
- 영상 FPS: cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
VideoCaputer객체의 read()는 마지막 Frame까지 차례로 Frame을 읽음
1
2
3
4
5
while True:
hasFrame, img_frame = cap.read()
if not hasFrame:
print('더 이상 처리할 frame이 없습니다.')
break
VideoWriter 개요
- VideoWriter 객체는 write할 동영상 파일 위치, Encoding 코덱 유형, write fps 수치, frame 크기를 생성자로 입력 받아 이들 값에 따른 동영상 Write 수행.
- VideoWriter는 write시 특정 포맷으로 동영상을 Encoding 할 수 있음(DIVX,XVID,MJPG,X264,WMV1,WMV2)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
cap = cv2.VideoCaputer(video_input_path)
codec = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
vid_size = (round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
vid_fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(video_output_path, codec, vid_fps, vid_size)
OpenCV 영상처리 실습
- OpenCV는 간편하게 비디오 영상처리를 할 수 있는 API를 제공
- VideoCapture 객체는 Video Streaming을 Frame 별로 Capture하여 처리할 수 있는 기능 제공
- VideoWriter 객체는 VideoCapture로 읽어들인 Frame을 동영상으로 Write하는 기능 제공
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 코랩 버전에서 위의 sample은 John wick이지만 실제 Video 처리는 강의와 동일하게 Night and Day로 수행.
import cv2
video_input_path = '/content/data/Night_Day_Chase.mp4'
# linux에서 video output의 확장자는 반드시 avi 로 설정 필요.
video_output_path = '/content/data/Night_Day_Chase_out.mp4'
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_input_path)
# Codec은 *'XVID'로 설정.
codec = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
vid_size = (round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))) #(200, 400)
vid_fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS )
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(video_output_path, codec, vid_fps, vid_size)
frame_cnt = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
print('총 Frame 갯수:', frame_cnt, 'FPS:', round(vid_fps), 'Frame 크기:', vid_size)
"""
총 Frame 갯수: 1383 FPS: 30 Frame 크기: (1216, 516)
"""
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
import time
green_color=(0, 255, 0)
red_color=(0, 0, 255)
start = time.time()
index=0
while True:
hasFrame, img_frame = cap.read()
if not hasFrame:
print('더 이상 처리할 frame이 없습니다.')
break
index += 1
print('frame :', index, '처리 완료')
cv2.rectangle(img_frame, (300, 100, 800, 400), color=green_color, thickness=2)
caption = "frame:{}".format(index)
cv2.putText(img_frame, caption, (300, 95), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, red_color, 1)
vid_writer.write(img_frame)
print('write 완료 시간:', round(time.time()-start,4))
vid_writer.release()
cap.release()
이 코드를 통해 동영상에 bounding-box가 그려지고 frame 변화하는 것이 보임. 예제 코드라 박스가 변하진 않음.
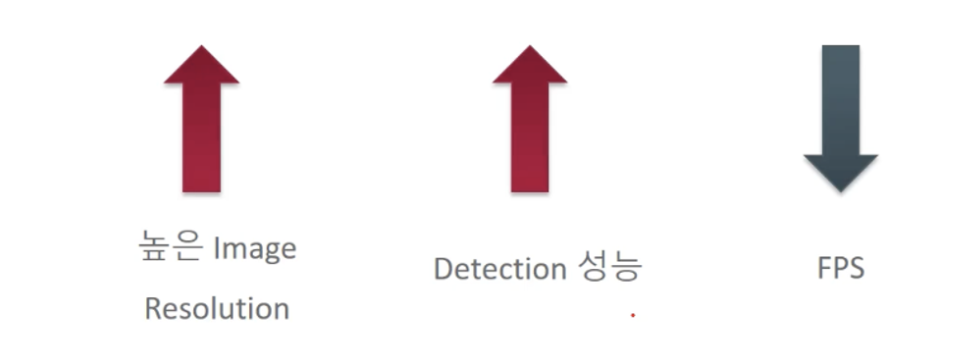
Image Resolution, FPS, Detection 성능 상관 관계
Image Resolution과 Detection 성능은 비례관계이고, FPS와는 상관관계이다.
FPS와 Detection은 반비례 관계이다.